Welcome to the official website of Yantai Changyun Electronics Co., Ltd.Tel:0535-6930766
DATE:【2018-03-19 13:46】 TIPS:【】次
XJAccelerator
Overview
The XJAccelerator is a multipurpose unit that can be integrated with your
XJTAG system to facilitate and accelerate programming functions as well
as extending test coverage on a Device Under Test (DUT).
Key Benefit
•Fast flash programming
•Increases board test coverage with additional interface connectivity
•Easy integration with XJTAG test systems
Features
•Reconfigurable
•FPGA board
•Supports SPI, IIC, ICSP, SWD and other protocols
•Supports NOR and NAND flash devices
JTAG controlled programmer
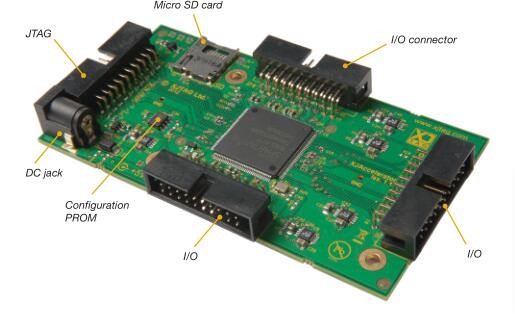
Based on a Xilinx Spartan 6 FPGA, the XJAccelerator card is principally designed to provide a versatile platform for accelerated programming applications. In this mode the FPGA is configured with XJFlash to program flash devices connected to any of the three I/O headers. The data to be programmed can either be streamed into the unit over JTAG or retrieved from a microSD card using the slot provided.
The FPGA can either be configured through its JTAG port, as part of a standard XJTAG project, or from the on-board PROM. To minimise the total time required for each board, the
configuration status of the FPGA is checked each time the project is run. Only if an unexpected status is found will the FPGA, or the configuration PROM be programmed.
Versatile and reconfigurable
The XJAccelerator card can be used to program standard NOR and NAND flash devices provided it is given access to all of the required signals. More bespoke programming operations are also possible providing the programing protocol can be replicated by the FPGA. XJTAG can provide XJFlash images that implement the following protocols:
•SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
•I²C/IIC – Philips/NXP Semiconductor’s Inter-IC bus
•ICSP – Microchip’s In-Circuit SerialProgramming
•SWD – ARM’s Serial Wire Debug
If the protocol you require is not listed here please contact us and we will be happy to investigate the possibility of adding that capability.
The unit is powered by an external 5V supply. The voltage levels for the three I/O connectors are user configurable from 1.2 V to 3.3 V.
Digital I/O testing
It is also possible to use the boundary scan capabilities of any unused signals on the three I/O headers for external digital I/O testing on a DUT.
Flexible connection
The XJAccelerator card can be connected to the JTAG controller in a number of different configurations allowing easy integration into a wide range of projects. It can be connected
to a separate TAP on an XJLink2-based JTAG controller or added in series with
the JTAG chain of the DUT.
XJComms
Overview
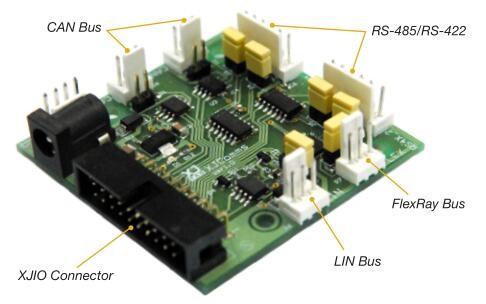
XJComms is a differential serial communications test card that allows you to extend the coverage that you can achieve using an XJIO Board.
You can test RS485 and RS422 interfaces, common to many designs, as well
as CAN, LIN and FlexRay which are all regularly used in the automotive sector.
Key Benefits
•Confirmation of signal integrity for common interface standards
•Increases UUT test coverage with additional interface connectivity
•Easy integration into XJEase
•Multiple boards can be used in the same project
Features
•Differential communications test card
•RS485/RS422, CAN, LIN, FlexRay
Digital Interface
The 20-way IDC header allows you to control and monitor each of the protocol transceivers. It is pin-compatible with the XJIO Board but can also be directly connected to an accessible JTAG enabled I/O connector on the UUT.
Test Control
Signals can be driven to or from the UUT to verify that both digital and protocol signals are correctly connected. Tests are implemented using standard XJEase scripts that are supplied with the card.
CAN Bus
The CAN (Control Area Network) serial bus was originally developed for use in automobiles, but CAN has found its way into other applications within modern vehicles, such as Body, Safety and Powertrain. It is also used in Avionics for cabin systems and instrument control panels (Airbus A380).
RS485/RS422 Bus
The RS485 standard specifies differential data transmission over a terminated twisted pair. RS485 is popular for inexpensive local networks, multidrop communication links and long haul data
transfer. The use of a balanced line means RS485 has excellent noise rejection and is ideal for industrial and commercial applications.
FlexRay™ Bus
FlexRay™ is a serial, bus system for real-time control applications and is designed for the future requirements of in vehicle networks. It has now migrated into aviation industry.
LIN Bus
By allowing a basic serial network connection between actuators, sensors or switches and an ECU, the LIN (Local Interconnect Network) bus has tremendously reduced the design efforts and costs for the car manufacturers. It is thus used in a fast growing number of applications, mainly
for low speed networking in Body and Interior applications.
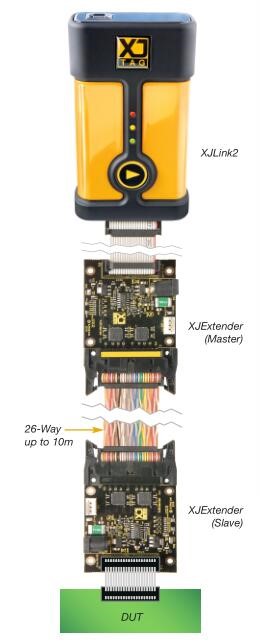
XJExtender
Overview
XJExtender is XJTAG’s recommended solution to overcome signal integrity issues when connecting an XJLink or XJLink2 JTAG controller to a remote Device Under Test (DUT). By using differential signalling, XJExtender allows you to work with a DUT up to 10 meters from the XJLink, even in electrically noisy environments.
Key Benefits
•Reliably extends the distance between XJLink/XJLink2 Controller and DUT
•Allows DUT testing in larger installations or environmental chambers
•Provides superior EMI immunity to preserve signal integrity
•Improves the overall performance of test systems
•Can be used with other XJTAG hardware including XJIsolator and XJXDP
Features
•Standard 26-way IDC connectors support cost-effective ribbon cable for board-to-board connection (twisted-pair ribbon cable recommended for best performance)
•TCK clock frequencies up to 50 MHz
•Flexible power supply voltage:5 V to 15 V(2 required, not included)
•Variable I/O voltage from 1.8 V to 3.3 V(when used with XJLink2)
•Provides 8 channels configurable as uplink or downlink (default configuration: 6 downlink/2 uplink)
•Master unit plugs directly into XJLink2 though standard 20-way IDC interface
•Slave unit connects directly to DUT using standard 20-way IDC socket
Extending performance
Poor signal integrity between an XJLink controller and DUT may force you to reduce TCK frequencies, or even stop you running tests.
The high levels of electrical noise that often exist in test environments can cause signal integrity problems when running JTAG tests; problems that can be made worse if a DUT has to be placed away from the XJLink, in a fixture or an environmental chamber.
XJExtender overcomes these issues by supporting cables up to 10 metres long without compromising signal integrity.
Flexible configuration
XJExtender comprises a Master unit connected directly to an XJLink controller, and a Slave unit connected to the DUT. Slave units can be purchased separately to support workflows that require Slave units to be permanently located within test fixtures.
Each unit offers 8 channels with a default configuration of 6 downlink (Master to Slave) and 2 uplink (Slave to Master). This can be reconfigured using on-board solder links to any combination of uplink/downlink channels.
Extending signal integrity
Using the Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) standard as the physical layer between the Master and Slave, XJExtender allows high speed communications over flat or twisted-pair
ribbon cables.
As each channel uses differential signalling, the cable generates low levels of Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR); important when testing sensitive electronic assemblies. It also exhibits very high immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), which enables the use of longer cables without loss of signal integrity.
Extended temperature range
The XJExtender units support an extended temperature range of -40 °C to +85 °C. This makes XJExtender the ideal solution for testing a DUT in an environmental chamber.
XJIsolator
Overview
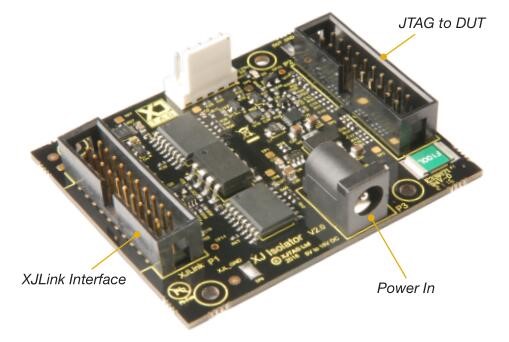
XJIsolator provides galvanic isolation between a Device Under Test (DUT) and a JTAG controller. Its small form factor means an XJIsolator board can be easily mounted inside a test fixture.
Key Benefits
•Provides high levels of galvanic isolation
•Compatible with all other test hardware from XJTAG
•Simple ‘Plug & Play’ installation
Features
•Isolation for voltages up to 443 Vrms
•Supports TCK clock frequencies up to 50 MHz
•Very low uni-directional propagation delay, typically 8 ns
•Single power supply required, referenced to DUT ground
•Flexible power supply voltage:5 V to 15 V
•Variable I/O voltages from 1.8 V to 3.3 V(set by JTAG controller or DUT)
•5 V I/O voltage option available
•Offers 8 isolated signal channels configured as 6 downlink and 2 uplink
•Requires no configuration in XJTAG software
•Compatible with XJExtender and XJXDP
Galvanic isolation
Galvanic isolation overcomes the challenge of connecting a test system to a DUT in situations where (either intentionally or unintentionally) they do not have a common ground. XJIsolator provides galvanic isolation for the Test Access Port (TAP) signals that are used
when testing a DUT with JTAG.
Plug & Play
XJIsolator easily integrates into a test set-up via its two 20-way IDC connectors using standard ribbon cables. It supports all of the TAP signals required for JTAG testing, passing them to and from the DUT.
The XJTAG’s JTAG controllers have an advanced auto-skew algorithm which
automatically compensates for the small additional delay introduced by adding the XJIsolator to a test set-up, making it simple to use and ‘invisible’ to XJTAG’s software.
Integrated power supply
The DUT side of XJIsolator runs at logic levels of 1.8 V to 3.3 V, set by reference voltage on the JTAG controller or optionally on the DUT. To isolate the DUT signals from the JTAG controller an external power supply (not supplied) is required, supplying 5-15 V DC.
Extending test capability
XJIsolator has been designed to work with XJTAG’s existing hardware and software products, including the XJLink2 and original XJLink JTAG controllers, and the complementary XJExtender and XJXDP boards. Combining these boards can address signal integrity issues and/or high drive strength requirements as well as galvanic isolation.
XJXDP
Overview
The XJXDP adapter complements the XJLink2 by providing a very low impedance drive capability, down to 25 Ohms or less. The small form factor board can be directly mounted onto an Intel ® eXtended Debug Port (XDP) for minimum wire lengths and maximum performance, or connected via a 2 mm 20-way ribbon cable.
Key Benefits
•Provides signal matching to improve JTAG performance
•High efficiency tracking power supply
•Supports non-XDP applications
•Optimised for performance
Features
•Direct connection to XDP port
•Flex cable option for tight access situations
•High signal integrity
•TCK clock frequencies up to 100 MHz
•Flexible power supply voltage:5 V to 15 V
•VTT tracking internal power supply
•Supported I/O voltages from 0.6 V to 3.3 V
•8 channels configured as 3 uplink, 5 downlink
•Plugs directly into XJLink2 controller
•Completely transparent to XJTAG software
Low voltage, low impedence
Some devices, notably Intel processors, use low voltage signaling with low value termination resistors typically in the range 0.8 V to 1.2 V and 25-50 Ohms. The XJXDP uses purpose designed low impedance drive circuits to get the highest noise margins and fastest JTAG
clocking speeds.
Precision line receivers
Precision, ultra-high speed comparators, with resistor-programmable hysteresis are used as uplink receivers for the highest receiver noise margin and speed performance.
Flexible
In addition to the XDP port connector, a standard 2mm pitch header is provided to allow ribbon cable connection for non-XDP applications. The XDP connector can also mate with a flex XDP-to-XDP extender cable.
Tracking power supply
The XJXDP uses a high efficiency tracking power supply to track the DUT’s VTT output (voltage reference), enabling it to drive low impedance downlink signals with minimal loading of the DUT. The XJXDP can be powered directly from the XJLink2 or from an external power supply.
Controlled rise/fall times
Low impedance downlink drivers can produce extremely fast edges that can cause undesirable overshoot, leading to loss of signal integrity and reliability. The XJXDP signal drivers moderate
rise/fall times to enable the highest clock speeds, with the greatest reliability and highest test throughput.
XJLink2 Compatible
The XJXDP connects to the XJLink2 (or XJLink) via a standard 20-way ribbon cable and level-translates 8 signals, divided between 3 uplink and 5 downlink.







